The world after the COVID-19 pandemic is unlikely to return to the world that it was. For the healthcare industry, radical changes have altered the landscape for everyone—payers, practitioners, and patients. Seemingly overnight, the industry was forced to rethink the way it worked and chart unfamiliar territories of remote working, telemedicine, and supply chain shortages.
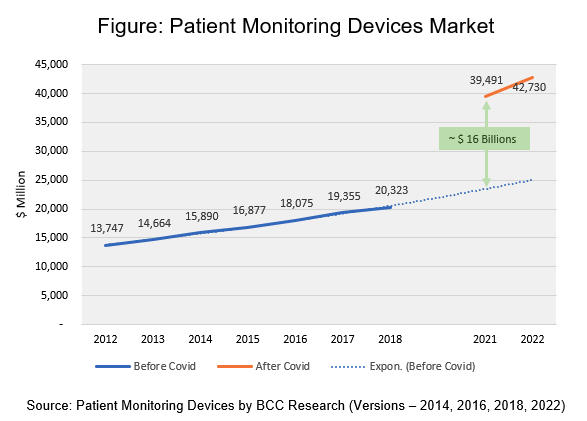
Three years on, healthcare systems have innovated faster than ever before. Healthcare visits are increasingly delivered remotely, even when patients have the option of in-person visit appointments. The demand for telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) programs skyrocketed. The patient monitoring devices market, projected to reach $23 billion by 2021 before the pandemic, jumped to $39 billion. A significant portion was contributed by RPM.
Overview of Current Trends in Remote Patient Monitoring
In 2022, the RPM market was primarily defined by increased market reach, greater patient and physician adoption, miniaturization of remote monitoring devices, worsening nursing shortages, rising demand for continuous monitoring, legislation changes, and a move towards deeper integration and centralization.
As the prevalence of chronic diseases like hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes grows, remote monitoring has become the most obvious and cost-effective way to reduce unnecessary emergency department visits and reduce the burden on the healthcare system. The convenience and fast access to care accelerated the adoption of RPM technologies among patients and practitioners, more so with miniaturization that made medical-grade monitoring devices compact and less invasive.
The Financial Crunch Facing Health Systems in 2023
Many healthcare organizations will be stepping into 2023 with significant regard for finances. Economic uncertainties and financial and operational issues will remain top of mind, with expenses estimated to soar by nearly $135 billion. Government grants and policy changes have supported many healthcare organizations. But the increasing labor cost, staffing crisis, supply chain challenges, and inflation are stretching the system beyond its capacity.
During the pandemic, healthcare organizations were innovating, but it is now time to reprioritize and look at surviving the crisis from a whole new perspective. Technology is one of the best ways to reduce healthcare costs while providing the appropriate patient care. Here’s how remote patient monitoring solutions can help alleviate some of the financial pressures:
- Reduce hospital readmissions by providing comprehensive virtual care solutions
- Improve patient outcomes by providing clear and continuous post-discharge instructions
- Reduce clinicians’ burden by leveraging remote solutions such as Hospital at Home
- Reduce the need for unnecessary emergency department visits through remote monitoring
- Improve the ability to provide value-based care
Successful Implementation of RPM in Reducing Healthcare Costs
Frederick Health’s Chronic Care Management program launched its telehealth program in 2017 to reduce readmissions and increase cost savings.
Challenges
- Improving patient outcomes
- Reducing readmissions
- Improving patient-provider communication
- Decreasing cost of service
Solution
A comprehensive telehealth and RPM solution that allowed the clinical team to:
- Monitor patient vitals and medication adherence
- Provide disease-specific education
- Improve patient-provider communication
- Perform check-in calls and virtual visits
Results
- Reduced hospital readmissions by 83%
- Cost savings of nearly $5.1 million
- Improved the quality of life of patients and their families
Now, let’s jump into the top 5 trends that will shape RPM in 2023:
Trend #1: RPM and AI
The healthcare industry's Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) market is expected to surpass $20 million this year. The increasing adoption of telehealth and telemedicine solutions significantly contributed to the growth of AI software solutions, which will likely continue for the foreseeable future.
AI makes health delivery more sophisticated by changing the way healthcare providers interact with patients. For remote patient monitoring, leveraging AI allows practitioners to predict, diagnose, monitor, and treat their patients from the comfort of their homes.
Trend #2: RPM in New Care Settings
Mental Health
Caring for mental well-being is as important as treating physical health. At least 4 in 10 adults in the U.S. were reported to have experienced psychological distress at least once since the COVID-19 outbreak. This year, RPM devices may be used to detect mental health issues through physical indicators such as activity levels, sleep patterns, and heart rate.
Pediatric Care
Pediatric patients and their caregivers leverage RPM to manage various healthcare issues, including asthma, diabetes, genetic conditions, behavioral health, neonatal care, and more. For children, providing care at a place they are most comfortable with can improve their health outcomes. RPM also provides flexibility and increased access for families with time and geographic limitations.
Trend #3: Expanded Use of Wearables
Wearable devices that monitor a patient's vitals, such as heart rate and blood pressure, are becoming more common in RPM. These devices can provide real-time data to healthcare providers, allowing more timely and effective care.
From Fitbit and smartwatches that can monitor heart rate and oxygen levels to more sophisticated devices such as ECGs, pulse oximeters, and blood pressure monitors, patients will be more equipped to receive care from home this year.
Trend #4: Greater Focus on Patient Engagement and Education
Patients with low health literacy levels are more likely to have poor health outcomes, make medication errors, have trouble managing their illness, make unnecessary hospital visits, and get readmitted.
RPM solutions are increasingly incorporating tools and resources such as teach-back videos and teleconsultations to help patients better understand their health and take an active role in their care. Practitioners are also including disease-specific materials into patient care plans to encourage them to be more proactive in their disease management.
Trend #5 Growing Importance of Data Security and Privacy
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) requires healthcare providers to protect patient’s sensitive health information from being disclosed without consent. However, HIPAA regulations around telehealth were relaxed during the pandemic to allow more flexibility in healthcare delivery.
As more sensitive health data is collected and transmitted via RPM systems, the need for robust data security measures will become increasingly important. Therefore, despite the relaxed regulations, telehealth and RPM providers like HRS continue to prioritize patient privacy and confidentiality.
RPM is here to stay and will play a critical role in the healthcare industry over the next few years. As technology advances, so will the need for tools that streamline processes for providers and facilitate better care for patients—and RPM is poised to take healthcare delivery to the next level.
Learn more about HRS’ RPM solutions today: https://www.healthrecoverysolutions.com/solutions
