The Complete Guide to Value Based Care
What is Value-Based Care?
Value-based care (VBC) is part of CMS (Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services) reforms in healthcare delivery and reimbursements, designed to incentivize the quality of care over the quantity of care. This means value-based care rewards providers for the value of care provided rather than the care volume.
Value is measured by delivered health outcomes and is geared towards health management, patient education, and consistent monitoring to identify and prevent health problems before they require treatment.
Doctors, hospitals, and healthcare providers are paid based on the patient's outcome and for improving a patient’s health. Today's standard is a fee-for-service model that is reactive to health issues, whereas VBC provides a proactive approach.
Why is Value-Based Care Important?
Value-based care is essential in improving the quality of care given to patients. It aligns the healthcare focus from quantity to quality—delivering better patient care, population health, and a more cost-efficient healthcare system.
This improved level of care leads to higher patient satisfaction and better health, more robust cost controls, reduced hospital visits and readmissions, and reduced healthcare spending for society.
In addition to these benefits, VBC addresses the historical imbalance of the fee-for-service healthcare model.
The fee-for-service model has led to the following:
- A skewed focus on the quantity of care over the quality of care
- Higher healthcare costs in the US, with total spending estimated to reach $6.2 trillion by 2028
- A mismatch between healthcare costs and health outcomes
How Does Value-Based Care Work?
Value-based care models reward or penalize healthcare providers based on quality and cost of care.
For example, the CMS will evaluate a hospital working under the value-based program on various criteria, like immunization rates for certain diseases, Medicare spending per capita, and patient feedback.
How the hospital scores in managing patient or population health against set benchmarks determine if the CMS will disburse additional funds on top of their fee structure or slash their Medicare allocation.
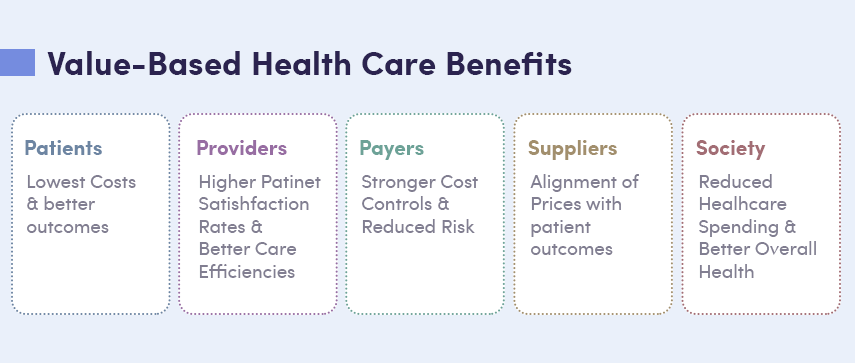
What are the Benefits of Value-Based Care?
Value-based reimbursement provides advantages for patients, healthcare providers, payers/insurance providers, suppliers, and the greater population.
There are five key benefits to implementing a VBC model:
Reduce the cost of care
Value-based care acts proactively to prevent health concerns and focuses on improving overall health leading to fewer emergency room visits, hospitalizations, and re-admissions. Patients simply spend less to get better with CMS value-based care.
Improve patient experience
Patients report a significantly better experience when the quality of care becomes the focus. Value-based care results in better treatment and bedside manner from providers.
Improve treatment quality
The criteria set for value-based payments to healthcare providers incentivize better care. The bar for satisfaction is constantly raised with Medicare value-based care.
Educate patients
With the focus of value-based care models on health management, patients need to be well-informed on methods, strategies, and practices to improve their overall health. The knowledge gained provides confidence and comfort for patients to have a better experience navigating the health care system.
HRS’ telehealth and remote patient monitoring (RPM) platform provides an all-in-one healthcare solution with added education focused on promoting patient independence and peace of mind. The platform uses advanced biometric monitoring and virtual visits to connect patients with care providers, along with features such as medication reminders, condition-specific education, and teach-back quizzes.
Reduce healthcare risks
The proactive approach of VBC prioritizes prevention so that health issues are addressed before they pose a severe problem. This model improves access to preventative treatments and monitors patients according to their risk factors.
What are the Value-Based Care Sub-Models?
The CMS has created sub-models of VBC for providers to implement. Some of these sub-models are:
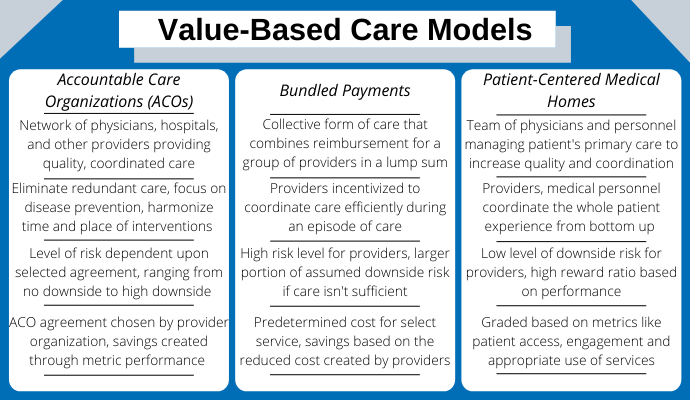
Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs)
Accountable care organizations comprise a network of care providers that help reduce healthcare costs by coordinating patient care. The Affordable Care Act encourages the adoption of this sub-model and is designed to reward quality of care.
Providers receive more reimbursement from Medicare if they consistently keep their patients in good health, and the network collectively becomes eligible for bonuses when they deliver this improved care.
Shared Savings Reimbursement Model
The shared savings reimbursement model is designed to reward the efficiency of care. To accomplish this, healthcare providers receive a fixed capital allocation to treat a patient for a specific condition or procedure for a fixed period.
If the provider can treat the patient in less time and for less than the amount allocated, they are entitled to any surplus.
If the cost exceeds the fixed amount or time, the provider can no longer bill for extra treatments per the fee-for-service model.
Patient-Centered Medical Homes
Patient-centered medical homes are designed to provide a conducive ecosystem to care for patients in their homes.
These medical homes are not single healthcare buildings but a network of care providers that support the patient led by a primary care physician. They utilize medical data capture capabilities of technologies like remote patient monitoring to ensure round-the-clock visibility of patient health.
This technology shares medical data amongst patient care teams to ensure efficiency while saving costs.
Value-Based Care and CMS
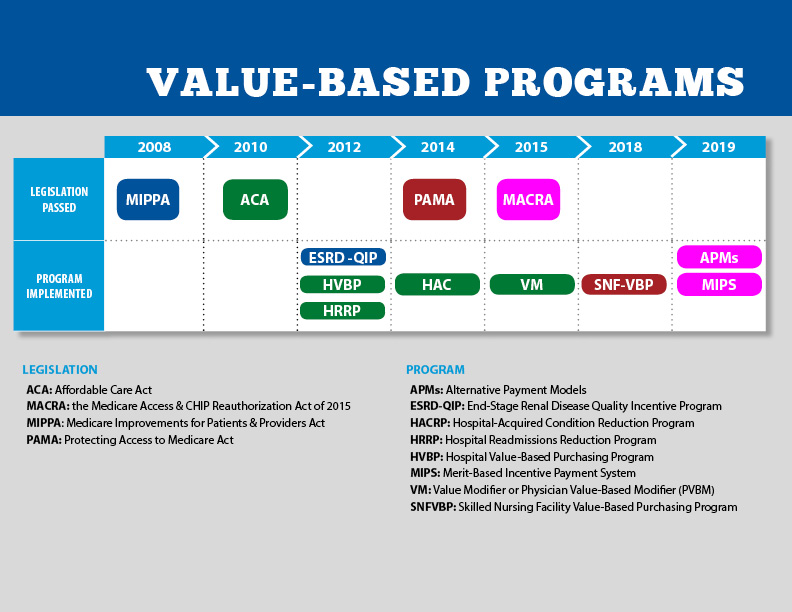
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services has been the leading proponent of value-based care. They have passed various legislations in recent years to promote a value-based care approach to healthcare. These include:
- MIPPA - Medicare Improvements for Patients & Providers Act (2008)
- ACA - The Affordable Care Act, also known as Obama Care (2010)
- HVBP - The Hospital Value-Based Purchasing Program (2012)
- HRRP - The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (2012)
- MACRA - The Medicare Access & CHIP Reauthorization Act (2015)
- MIPS - The Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (2019)
CMS has also introduced various other value-based care models, such as:
- End-Stage Renal Disease Quality Incentive Program - Promotes the delivery of high-quality care by dialysis facilities.
- Hospital Value-Based Purchasing (VBP) Program - Holds healthcare providers to higher standards for cost and quality, reducing unnecessary methods of care while rewarding the most efficient and effective healthcare providers.
- HRRP - Encourages providers to educate and engage patients and caregivers to reduce avoidable hospital readmissions.
- Value Modifier Program (VPM) - Provides differential payment to physicians based on the cost and quality of care provided during a set performance period.
- Hospital Acquired Conditions Reduction Program - Helps link Medicare payments to healthcare quality, evaluating hospital performances using weighted average scores.
Value-Based Reimbursement and Cost-Savings
There are numerous reimbursement models in the healthcare providers industry, including:
- Value-Based Care
- Fee-for-Service
- Bundled Payments
- Capitated Payments
- Population-Based Payments
Value-based care results in significant cost savings over time compared to the other healthcare reimbursement models.
Because of the nature of better care and consistent monitoring in value-based care systems, there are fewer readmissions, fewer hospitalizations, and fewer trips to the emergency room. This alone drastically reduces the cost of healthcare for a population.
Significantly less time, money, and effort are used when patients are treated more efficiently and are guided to seamlessly progress through the integrated care ecosystem.
Contrary to the other healthcare reimbursement models, the health outcome-based and bundled payments with VBC discourage unnecessary treatments and extra billings.
How to Implement Value-Based Care Models
There are seven key steps to implementing a value-based care model.
These are:
- Identify patient population and needs
Understanding patients' health needs and requirements are critical for providing the appropriate care to the population. Structuring services around common and routine problems allows for more efficiency, better integration, and healthier and happier patients. - Design appropriate care solutions
After identifying the patient population and needs, providers can design more tailored solutions that deliver the highest level of care. Focusing on this design ensures better patient health outcomes by allowing appropriate follow-up and necessary preventative maintenance. - Build integrated knowledge teams
Something as complicated as patient health requires integrated teams that support each other around one common goal—providing the most value to patients. Teams of experts will span across several medical disciplines and physical locations using numerous technologies and systems.
To integrate your healthcare systems, teams must be integrated and centered on achieving a common goal together.
- Quantify health outcomes and costs metrics
Two metrics must be measured and evaluated for a successful and valuable relationship between patients and providers. Quantifying health outcomes and cost metrics provides the data and insights to know the value of care and areas to improve care and efficiency. - Develop partnerships with technology and healthcare providers
A key to providing an integrated value-based care model is to take advantage of the expertise and excellency of different technology and healthcare providers. Developing these partnerships provides patients with the support and care they need across all necessary disciplines while benefiting the providers with reduced costs and improved efficiency. - Educate providers and patients
Value-based healthcare relies so much on integration. Ensuring the entire team is educated about the role they are executing and how it fits into the larger health program is required to provide an elite level of care meeting CMS and patient standards.
Patients and providers who are adequately educated on the desired outcome can make the best decisions to achieve that goal.
- Measure and improve
Consider the best medium of education—be it physical or digital—and leverage virtual visits when appropriate
Barriers to Entry when Implementing Value-Based Care Models
Three major barriers to implementing VBC models need to be addressed and avoided.
These are:
- Lack of resources (staffing, equipment, etc.)
- Difficulty collecting and reporting patient information
- Interoperability (internally and externally)
These barriers can be easily overcome using remote patient monitoring and telehealth services and solutions, such as those provided by Health Recovery Solutions (HRS).
Using RPM significantly impacts the efficiency of providers' resources, such as staffing constraints. Remote patient monitoring allows a single telemonitoring clinician to care for a ratio of approximately 80-100 patients.
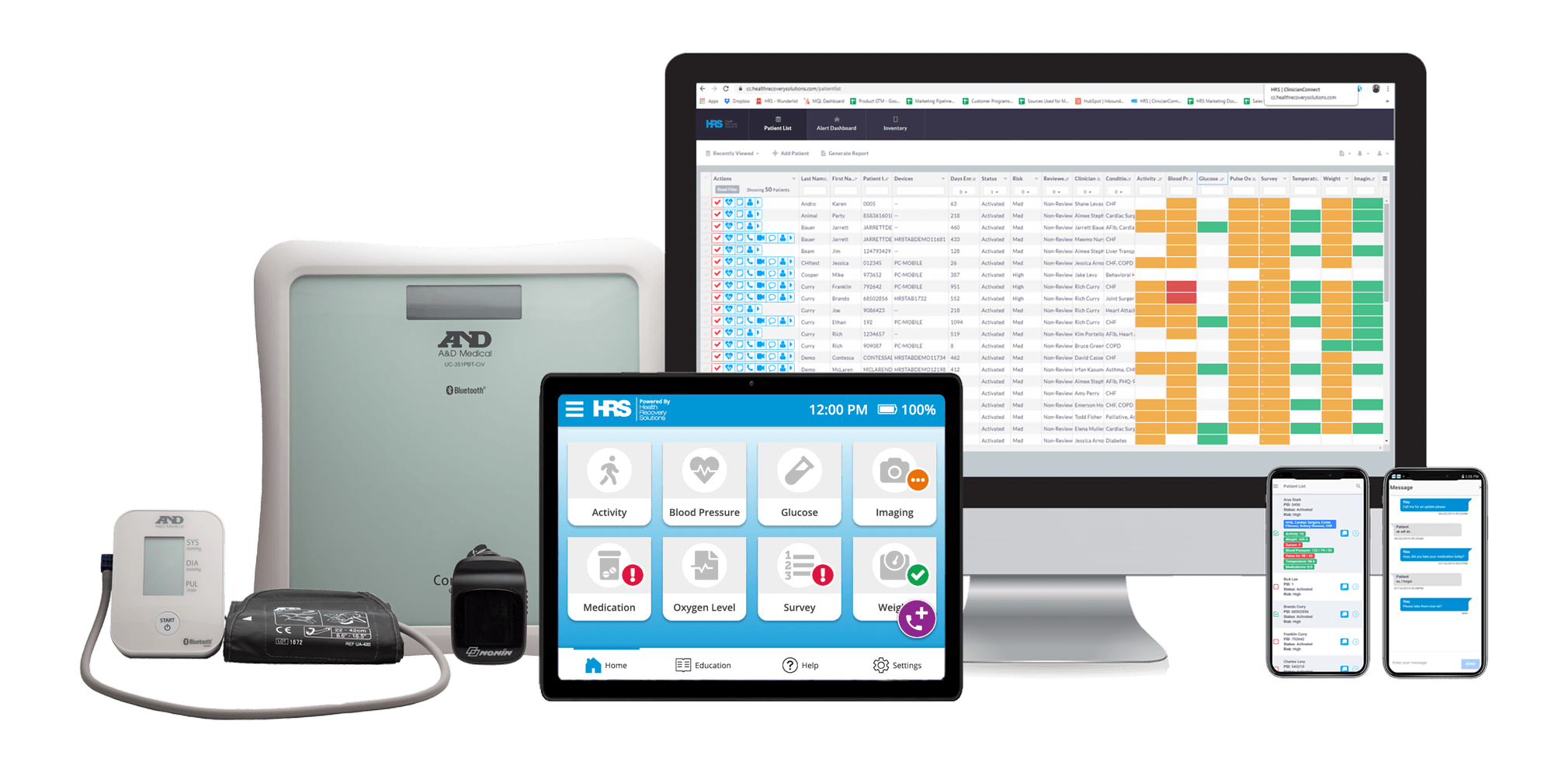
HRS has industry-leading solutions taking a hospital-at-home approach, supporting patients without visiting the hospital or office. With PatientConnect ®, patients are given a simple and ready-to-use tablet and advanced biometric device, equipping them with all the tools for communication, vital sign monitoring, education, medication tracking, and more.
Health Recovery Solutions also provides a complete logistics and inventory management service, PatientDirect ®, enabling patients to get up and running quickly while handling the time-intensive process of sanitizing, provisioning, shipping, and calibrating equipment.
While collecting, reporting, and sharing patient information accurately and timely is difficult, HRS has a single integrated system. The all-in-one platform securely collects, tracks, stores, and sends electronic health records to all necessary parties, internally and externally, removing vast amounts of administrative work.
Value-Based Care is Here to Stay
There is a significant opportunity within the healthcare system to improve the quality of care while reducing costs for both patients and providers.
By incentivizing performance instead of profit margin, VBC steers providers to provide care with the best outcomes instead of the highest cost. This has laid the groundwork for accountable quality care—a better way to do healthcare.
The future of quality health care is value-based because of the reduced cost of care, improved patient experience, and improved treatment quality.
Data and Digital Tech Enabling VBC
Data analysis and breakthrough digital technologies are playing an integral part in enabling explosive growth within VBC via:
- Online and mobile knowledge sharing and delivery
- Wearables data capture and remote monitoring capability
- Telemedicine’s off-site care delivery
Technologies such as remote patient monitoring create the impetus for a data-driven approach to medical care, giving providers actionable insights, greater visibility, and innovative ways to create value for patients, medical establishments, and healthcare in general.
What’s Next for VBC?
The continued transition to value-based care faces many challenges. To navigate the hurdles and become successful in the virtual-based care environment, healthcare providers require a complete and integrated solution like the HRS telehealth and remote patient monitoring platform.
Want to learn how telehealth & RPM can help you improve your value-based care? Talk to a digital health specialist today!
Ready to get started on your telehealth program? See how our comprehensive solutions fit in with your healthcare goals.
Download the 6 Essential Steps to Building a Scalable and Profitable Telehealth Program White Paper

In this white paper, learn about:
- Establishing goals
- Determining your financial plan
- Choosing a technology partner
- Building clinician and patient buy-in
- Other essential factors to consider to ensure your program is successful
